Planning Phase
Various underwater excavation works was required; dredging/removal of soil, demolition of grout blocks, silt suction/removal and removal of horizontal and vertical blinding layers with various material strength. The variety in material made the preparation phase demanding in terms of selection the most proper tooling. Several site visits and substantial hours of testing was performed prior to the operation to optimize the project execution.
Challenges
- Various soil/ layers to be removed
- Sand
- Mud/clay
- Grout piles (Grid, 1,5 x 2m)
- Horizontal and vertical steel and plastic pipes
- Reinforced concrete blinding layer
- GEWI uplift anchors (not to be damaged)
- 0-5cm visibility
Specific Tooling
A 20Te Scanmachine spread and various tooling was shipped to Berlin
- Extra long suction nozzle (2m)
- Xcentric ripper
- Drum cutter
- Telescopic arm
- 3D sonar to deal with the limited visibility
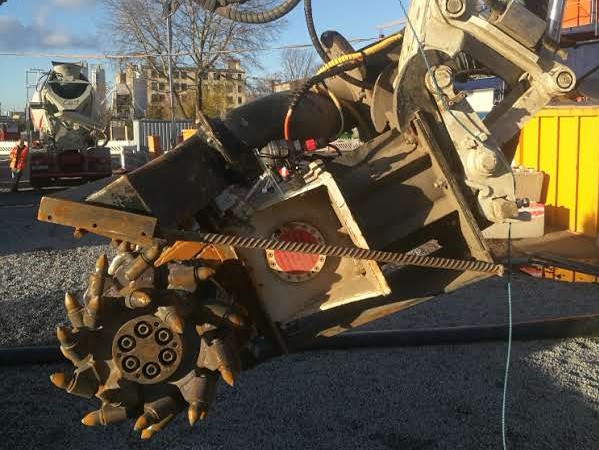


Image Caption: Xcentric ripper
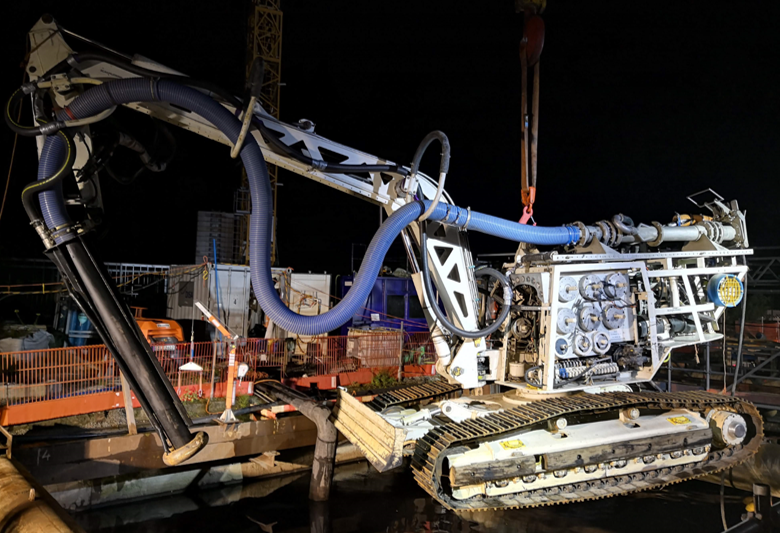

Image Caption: 2m suction nozzle

Project Execution
Dredging of mid layers
- Scanmachine 2 fitted with Erkat drumcutter
- Used to cut grout into smaller pieces
- Fitted with suction nozzle to dredge out material
- Slurry pump was used to transport soil. The soil was transported up to 70m horizontally and 25m vertically to a topside separation plant.

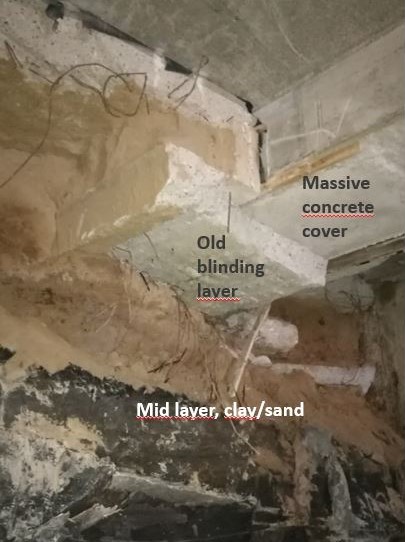
Removing old blinding layer
- Scanmachine 2 with telescopic arm and Xcentric Ripper
- Used in horizontal movements, ripping down blinding layer in the ceiling without damaging the massive concrete cover.
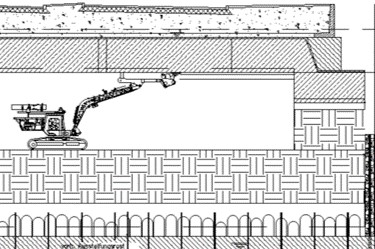
Image Caption: Ripping the ceiling
Dredging around GEWI piles – bottom layer
- Special care was to be taken – GEWI piles should not be damaged
- 2m suction nozzle with HF jetting was utilised (ref image)
- GEWIs (Steel anchors) in a grid of 3 x 2,5m
Controlling the operation in zero visibility
- Scanmudrings real-time monitoring system provided a virtual working environment for the operator
- Dual depth sensors were used to provide accurate dredging depth
- Various camera’s monitoring the area and separation plant gave the operator knowledge about production rate
- A separate tripod equipped with a CodaOctopus Echoscope 3D sonar was used as an acoustic camera to navigate in the tunnel. This was also used to create interim surveys of the dredged area

Conclusion / Lessons Learned
- The project was executed in a safe manner and in good cooperation with both divers and the construction company.
- Using the Coda Echoscope sonar was good for overall positioning and provided the operator with real-time view of the surroundings
- Dual depth sensor setup provided accurate depth measurements
- Several methods and tooling were tested and utilised for the various levels, both prior to the project, but also during project execution dealing with new challenges along the way
The project was also presented on German news:



